Bolted steel structures
Bolted joints comprise fasteners secured in place by mating threads, to connect or attach parts of a structure together.
Bolting is the major alternative to welding for connecting structural steel and has become the most widely used, versatile and reliable method of making field connections in structural steel members.
In bolted steel structures the bolts, nuts and washers are critical items on which the integrity of the entire structure depends.
For exterior use these critical fasteners must be adequately protected from corrosion. Where steel members of the structure are galvanized it is preferable that fasteners employed should also be galvanized or suitably zinc coated to maintain a uniform level of corrosion protection throughout the structure.
Bolting in hot dip galvanized steel structures
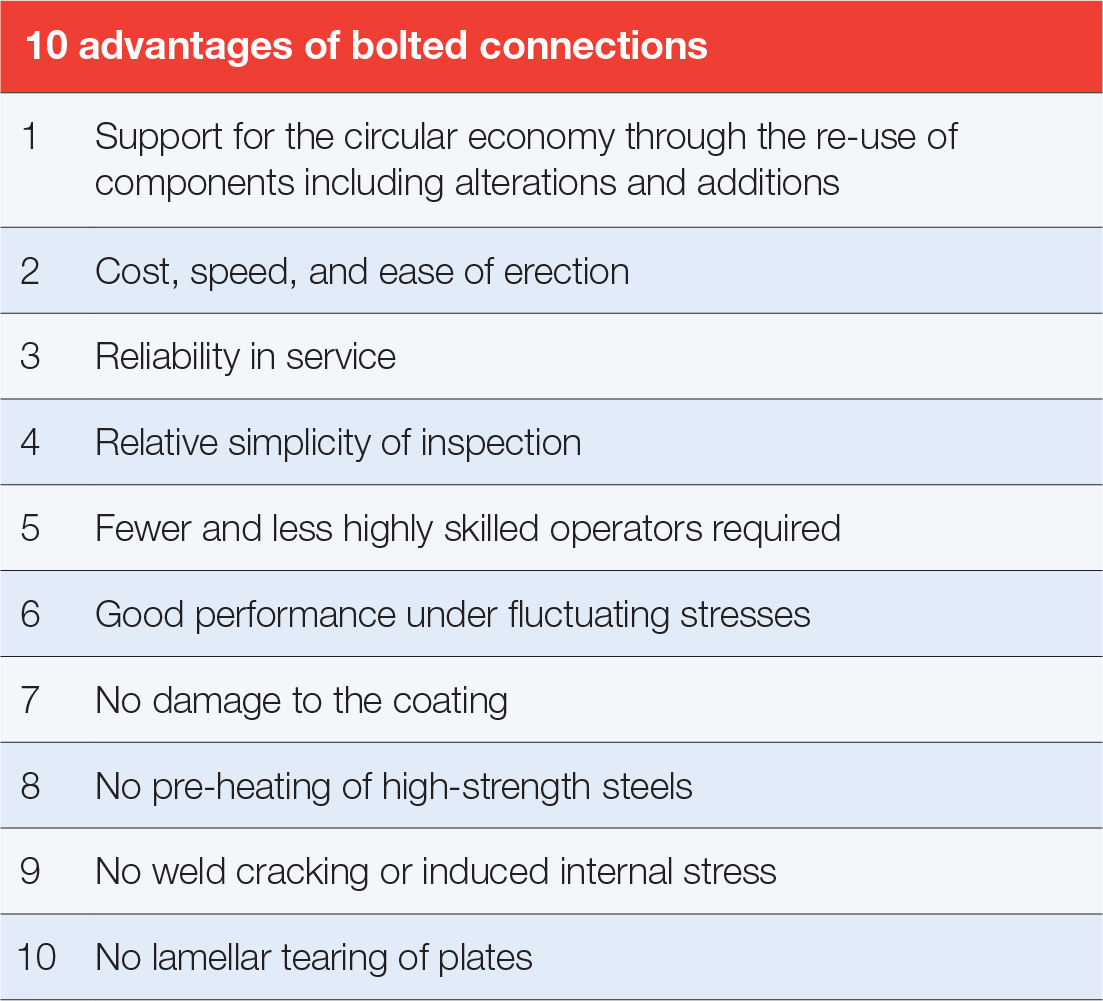
In the construction of steel structures, bolted connections offer significant advantages over other construction methods. For galvanized structures, bolted connections eliminate the damage that occurs from local heating of the surface during on-site welding and with it the need for coating repairs to the affected area.
The high cost of maintenance labour and wide use of steel communications towers, steel framed buildings, industrial structures, steel bridges and power transmission (often in remote areas) have made low maintenance corrosion protection systems an essential aspect of design. As a result, hot dip galvanizing has become the accepted standard for exposed steel, placing greater emphasis on bolted joints for structural steelwork and leading to development of specialised bolting techniques.
A wide range of hot dip galvanized, sherardised and zinc plated structural bolts and related fittings are available to meet any steel construction need.
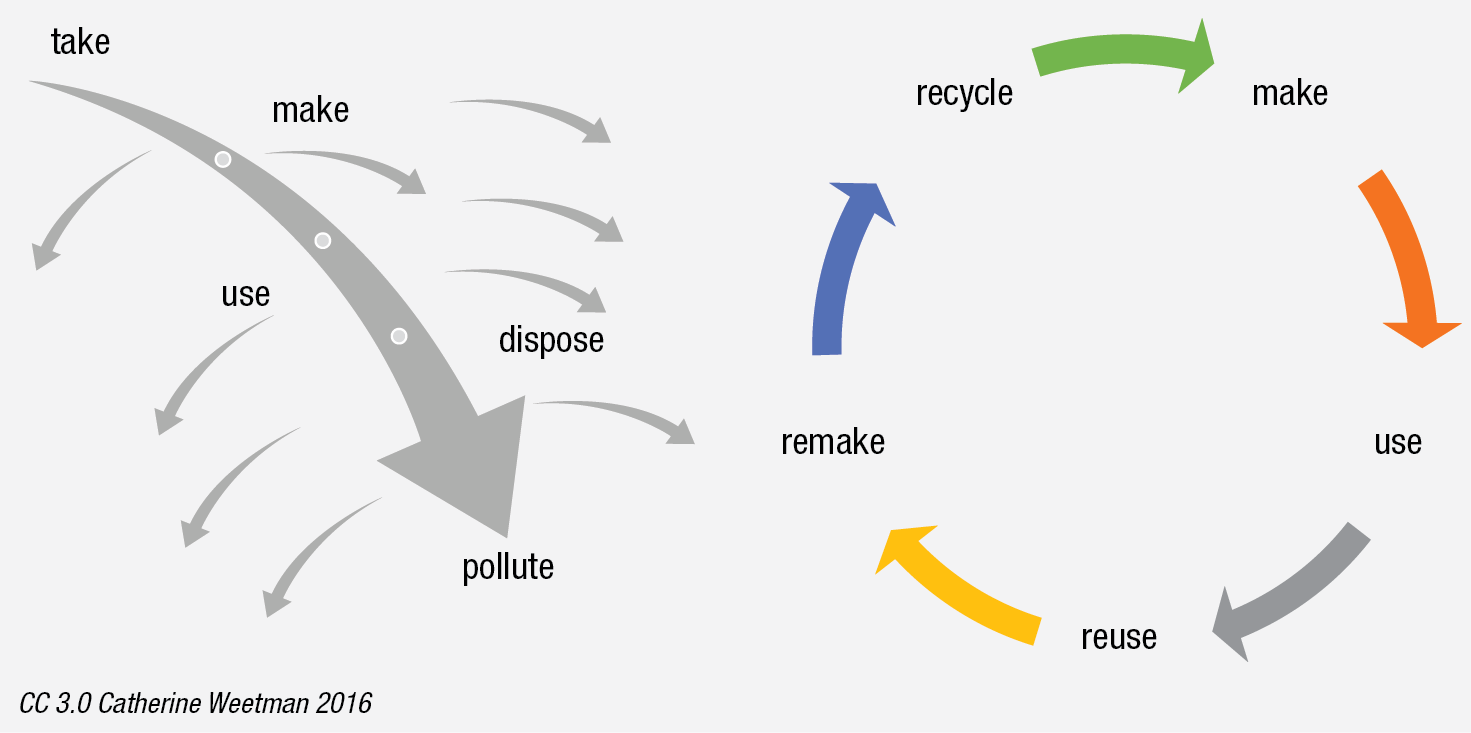
Another advantage of bolted connections are their viability in a circular economy in the re-use phase, as they allow the original structure to be designed in modules leading to smaller, transportable, demountable structures which are suited for galvanizing and re-galvanizing and therefore are more sustainable than other coatings.